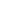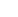Lung cancer is characterized by the highest incidence rate and mortality rate among malignant tumors in China, and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of the lung cancer, accounting for about 80%-85% of the total incidence.
MRG003 is currently the first-in-class domestic ADC drug targeting EGFR under clinical research. In a phase II clinical trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of MRG003 among EGFR positive advanced NSCLC patients, 3 patients (including patients with EGFR mutation and driver gene mutation- negative), who experienced progressive disease (PD) after receiving EGFR-TKI or chemotherapy for more than one year, were enrolled in the MRG003 treatment arm. These patients only received two sessions (6 weeks) of MRG003 treatment and were found that the total diameter of their target lesions reduced by more than 50% and these patients were all considered to achieve partial response (PR).
These results indicate the encouraging therapeutic activity of the drug, which powerfully verifies the therapeutic profiles of MRG003 to effectively overcome EGFR resistance mutations, provides a new therapeutic concept for second-line treatment of patients with driver gene mutation-negative NSCLC, and suggests that MRG003 may be independent of ALK, ROS1, BRAF, cMET, NTRK and KRAS status and have the potential to define a new standard of care when treating PD-L1 expressed tumor types.
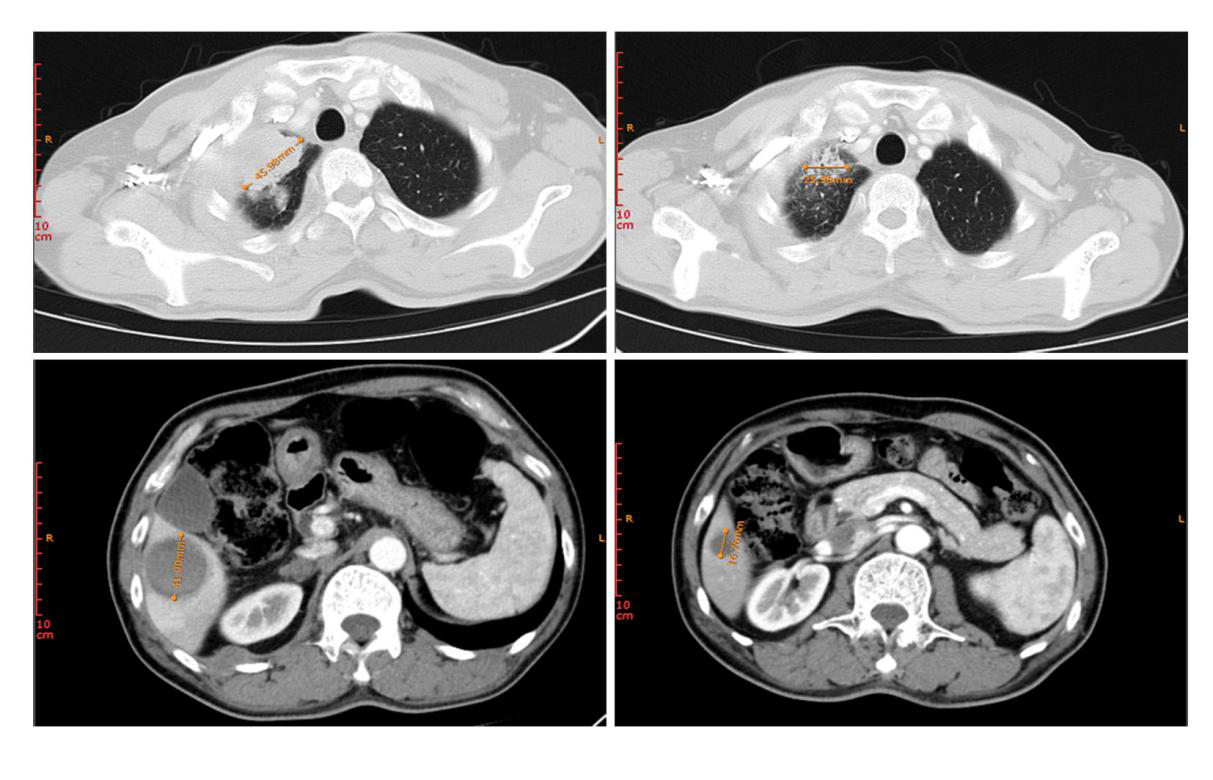
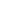
Figure 1. Changes in lesion of patient 1 before treatment (top left: lesion in the superior lobe of right lung; bottom left: liver metastases) and after treatment (top right: lesion in the superior lobe of right lung; bottom right: liver metastases)
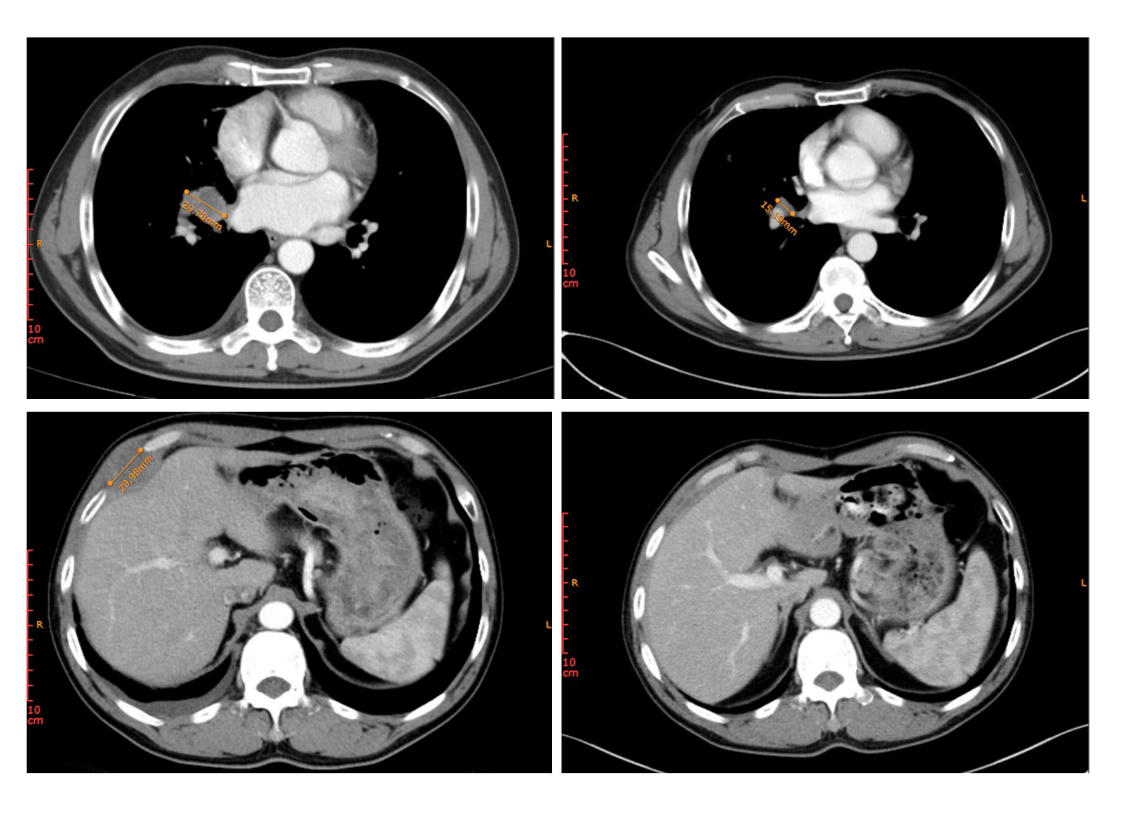
Figure 2. Changes in lesion of patient 2 before treatment (top left: lesion in the right hilum; bottom left: metastatic tumor in the right chest wall) and after treatment (top right: lesion in the right hilum; bottom right: metastatic tumor in the right chest wall)
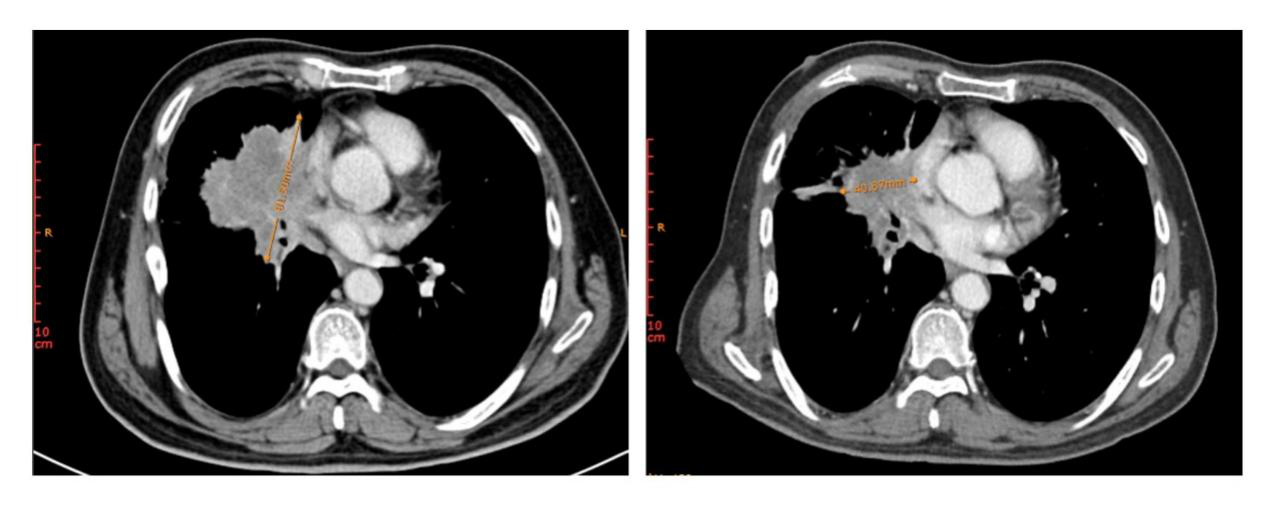
Figure 3. Changes in lesion in right hilum of patient 3 before treatment (left) and after treatment (right)
Source from YXJ(Shanghai Yimi Information Technology Co., Ltd.)